Descrição
Goal: H2CORK will develop novel CeO2-based Ecoceramics, exploiting the regular, highly porous microstructure of sustainable cork templates, for the innovative renewable production of hydrogen via direct solar thermochemical fuel production (TCFP).
Sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, such as H2, are urgently needed, and must be produced using renewable energy to be truly sustainable. Concentrated solar energy (a focused beam of sunlight) can be used to produce electricity, split water or create synthetic fuels without CO2 emissions. H2 production via direct solar TCFP should be more efficient than electrolysis using solar electricity, and so is an innovative solution to H2 production. What is required is a suitable material for a TCFP catalyst.
It is known that CeO2-based materials can be used to split water and produce H2 for TCFP, via a redox cycle that requires heating up to 1400 ºC. What is required is further development and optimisation of such materials to improve efficiency and redox reaction rates, and to enhance their microstructure/surface area. Any materials solutions should also be based on renewable/sustainable resources and methods.
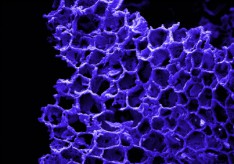
This will be achieved by developing innovative CeO2-based catalysts with enhanced regular 3DOM microstructures using naturally occurring cork templates to create Ecoceramics (Environmentally conscious ceramics). These will be a novel form of biomimetic material using a cork template, to make a ceramic with the unique, highly porous cellular microstructure of cork.Cork is a totally sustainable Portuguese resource, the bark being harvested without damaging the tree, which lives on to sequester CO2 for centuries.
Methods: Solar Energy Materials, Solar Energy, Biomimetics, Biomimetic Materials, Concentrated Solar Power, Water Splitting, Hydrogen Production, Sustainable Energy, Materials for Sustainable Energy, cork, ceria, biomimetic ceramics, sustainable materials, thermochemical fuels production, ecoceramics, CeO2, hydrogen production
Coordenador
Coordenação
Universidade de Aveiro (UA)
Participantes
LNEG
Grupos
G5 - Materiais Biomiméticos, Biológicos e Vivos;
G4 - Materiais Renováveis e Economia Circular;
Resultados
Robocasting of 3D printed and sintered ceria scaffold structures with hierarchical porosity for solar thermochemical fuel production from the splitting of CO2
Ben-Arfa, BAE; Abanades, S; Salvado, IMM; Ferreira, JMF; Pullar, RCCork-derived hierarchically porous hydroxyapatite with different stoichiometries for biomedical and environmental applications
Scalera, F; Quarta, A; Tobaldi, DM; Pullar, RC; Piccirillo, CBiomimetic calcium carbonate with hierarchical porosity produced using cork as a sustainable template agent
Scalera, F; Carbone, L; Bettini, S; Pullar, RC; Piccirillo, CHigh performance cork-templated ceria for solar thermochemical hydrogen production via two-step water-splitting cycles
Oliveira, FAC; Barreiros, MA; Haeussler, A; Caetano, APF; Mouquinho, AI; Silva, PMOE; Nova, RM; Pullar, RC; Abanades, SSolar Redox Cycling of Ceria Structures Based on Fiber Boards, Foams, and Biomimetic Cork-Derived Ecoceramics for Two-Step Thermochemical H2O and CO2 Splitting
Haeussler, A; Abanades, S; Oliveira, FAC; Barreiros, MA; Caetano, APF; Novais, RM; Pullar, RCSustainable and efficient cork - inorganic polymer composites: An innovative and eco-friendly approach to produce ultra-lightweight and low thermal conductivity materials
Novais, RM; Senff, L; Carvalheiras, J; Seabra, MP; Pullar, RC; Labrincha, JAPyrolysed cork-geopolymer composites: A novel and sustainable EMI shielding building material
Novais, RM; Saeli, M; Caetano, APF; Seabra, MP; Labrincha, JA; Surendran, KP; Pullar, RCA Review of Solar Thermochemical CO2 Splitting Using Ceria-Based Ceramics With Designed Morphologies and Microstructures
Pullar, RC; Novais, RM; Caetano, ARF; Barreiros, MA; Abanades, S; Oliveira, FACA sustainable multi-function biomorphic material for pollution remediation or UV absorption: Aerosol assisted preparation of highly porous ZnO-based materials from cork templates
Quarta, A; Novais, RM; Bettini, S; Iafisco, M; Pullar, RC; Piccirillo, CSolar thermochemical CO2 splitting using cork-templated ceria ecoceramics
Oliveira, FAC; Barreiros, MA; Abanades, S; Caetano, APF; Novais, RM; Pullar, RCExtremely fast and efficient methylene blue adsorption using eco-friendly cork and paper waste-based activated carbon adsorbents
Novais, RM; Caetano, APF; Seabra, MP; Labrincha, JA; Pullar, RCUncovered: Ecoceramics
Pullar, RC; Novais, RMFinanciadores