Abstract
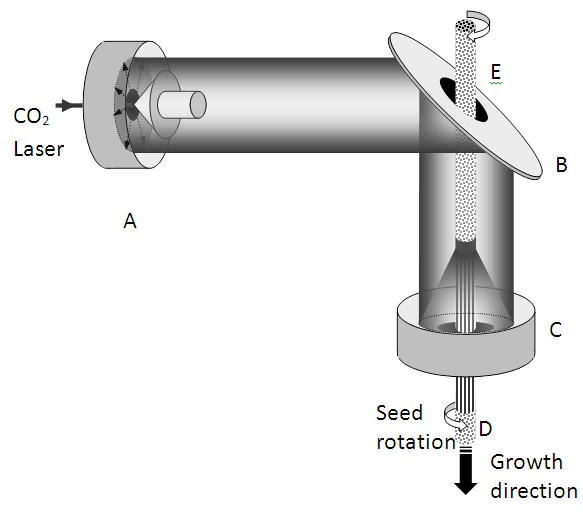
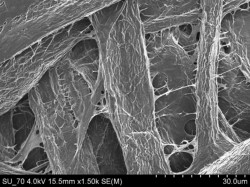
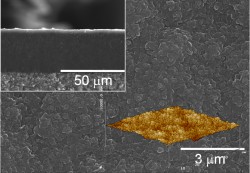
The mixed ionic-ionic type conductors in this invention are eutectic ceramics represented by the formula (BaZr1-xMxO3-x/2)1-z (Zr1-yMyO2-y/2)z wherein M is at least one element selected from the group of rare earth elements (Y, Sc, Ga), Al and In, with 0.03 ≤ x ≤ 0.20 and 0.03 ≤ y ≤ 0.20, and z being such that the Ba overall ratio compared to Zr in the composite in molar fractions is 0,21:0,79 ≤ Ba:Zr ≤ 0,29:0,71. These materials exhibit an eutectic type morphology comprising a mixture of a proton conductive phase (BaZr1-xMxO3-x/2) and an oxide conductive phase of oxygen-ion (Zr1-yMyO2-y/2), which are responsible by the composites ionic-ionic type mixed conductor behavior. These mixed ionic-ionic type conductors are synthesized by a directional solidification method referred as Laser-Floating-Zone (LFZ), allowing the simultaneous growth of proton-oxygen ion conductive phases without grain boundaries, a problem so far unsolved by conventional powders technology synthesis techniques.
Innovative aspects & main advantages
The invention discloses novel mixed ionic-ionic conductors synthesized by a directional solidification method referred to as laser zone melting (LZM), allowing simultaneous growth of protonic and oxygen ionic conductive phases without grain boundaries, a problem so far unsolved by conventional powder technology synthesis techniques.
Applications
Electrochemical devices, such as a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) or a solid oxide electrolyser cell (SOEC) and other related electrochemical technologies.