Abstract
The present invention relates to the obtainment of refractory ceramic bodies through different conformation processes, from aluminous sludge from waste water treatment plants (WWTP) of surface treatment, anodizing and lacquering aluminum industries.
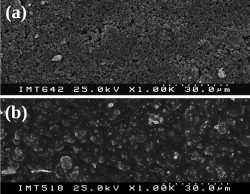
The sludge, as it exits the WWTP, can be used as raw material in the formulation of ceramic compositions, dried at 110 ºC, calcined at elevated temperatures (1200-1400 ºC) or, alternatively, after calcination at lower temperatures (up to 800 ºC) followed by wash to remove soluble salts.
After the adjustment and control of the pulp characteristics, incorporating the aluminous residues, clay materials and/or diatomite, it is possible to conform ceramics pieces by dry pressing (atomized powders) for filling (traditional or under pressure) and by plastic conformation (extrusion, pressing).
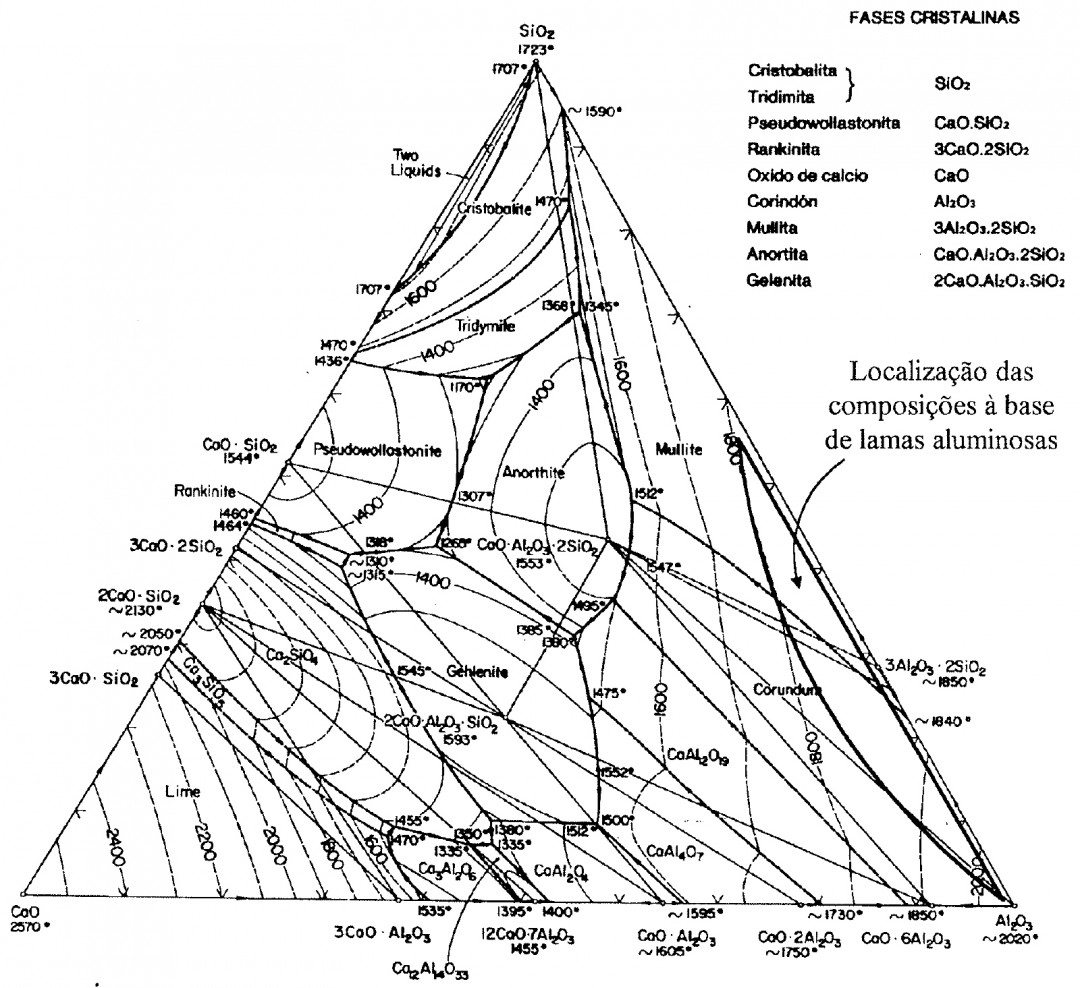
By this invention we obtain ceramic refractory bodies of diverse applications, based on mullite and/or alumina.
Innovative aspects & main advantages
The novelty consists on reusing an alumina-rich industrial sludge in the fabrication of refractory ceramic bodies through different conformation processes, with all associated advantages of reducing the amount of waste material sent for land fill and adding it a new value. The reprocessed sludge can be used alone or in combination with other industrial wastes or raw-materials to adjust the consolidation process and the intended properties of the final refractory materials.
Applications
The mullite-alumina based refractory ceramics produced according to the present invention are suitable as for structural materials for high temperature applications.